
Intro
Imagine that you need to create a simple frontend project, easy to build and deploy, where all will be statically generated and served by a content delivery network (CDN). Beautiful. Now, your application is growing that one day you wake up and "Ok, maybe I can implement a Newsletter" or "In addition to exposing the products, maybe I also allow online payments, why not?".

BOOM! Thousands of technologies spread on your face: server, AWS, Postgres, secrets, Heroku, apache, DNS, gateway, potatoes, and so on. Inevitably, a backend is needed in this context!
Given this, we have at least two possible ways: develop the entire backend infrastructure which offers this new functionality, ensuring security, maintenance, and scalability, OR hire a serverless service that takes care of everything but the kitchen sink.
Serverless
First of all, the first way is entirely possible and often necessary. However, I want to introduce you to Serverless or Serverless computing's concept and how it may be helpful. According to Martin Fowler's Serverless Architectures article, there are two approaches to this topic.
- Backend as a Service (BaaS)
Third-party, cloud-hosted applications and services, to manage server-side logic and state. In this case, the application/client connects with the backend only to "consume" the resources provided by these services. For example, Auth0's authentication and authorization ecosystem is a security abstraction for the front end. Firebase (Google) is another example: in addition to security, this ecosystem also provides storage.
- Functions as a Service (FaaS)
Applications where server-side logic is still written by the application developer, but, it’s run in stateless compute containers. In other words, the ecosystem provides a "space" to run part of your application's code that could not run on the front end side. Note: This processing will only happen on demand (event) and after execution, it is finished, that is, there is no infrastructure running all the time. Although this service is also called Lambda Functions or Lambdas Edges, it has become well known mainly for its implementation of AWS Lambdas.
Without a doubt, Amazon, Microsoft, and Google are major references on the subject for investing a lot of time and money. But, there are also other companies and services with good technologies to talk to, like Vercel and Netlify.
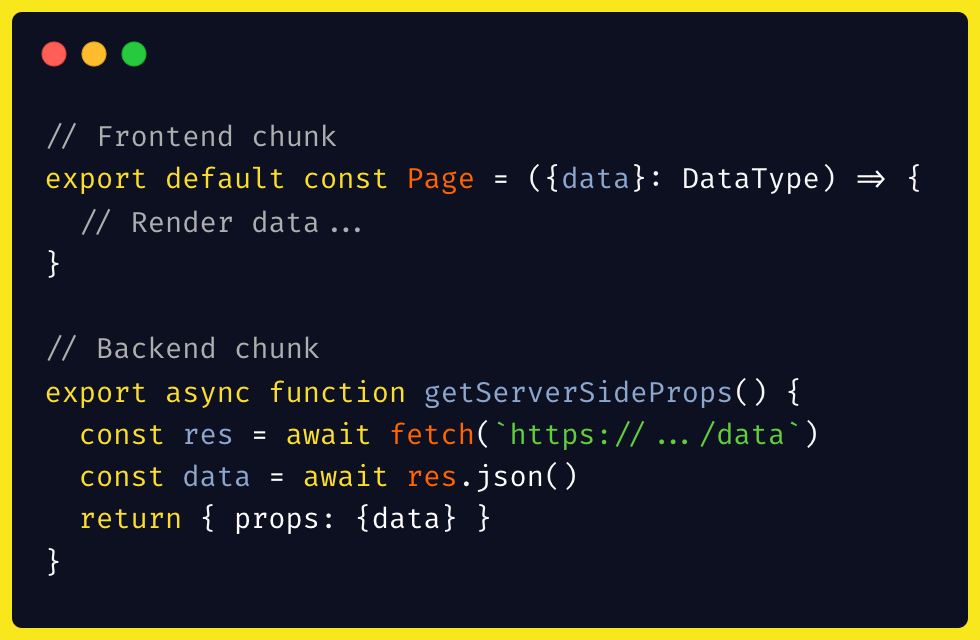
Vercel offers a slightly different hosting model than the common one. I mean, part of your service is to provide processing space for functions (Js, Go, Ruby, PHP, etc.) that cannot run on the front end of the hosted application (FaaS). In practice, it is possible to incorporate part of the advantages of a backend without the need to develop one with Node + Express application, for example.
As such, when developing a front end application with NextJs (and MongoDB Cloud Service), each file inside the /api folder becomes a serverless function, being a route that the application can access, which when started, a piece of code is processed on the server side. For instance, a simple API controller. Following the example of the introduction, we would have something like:
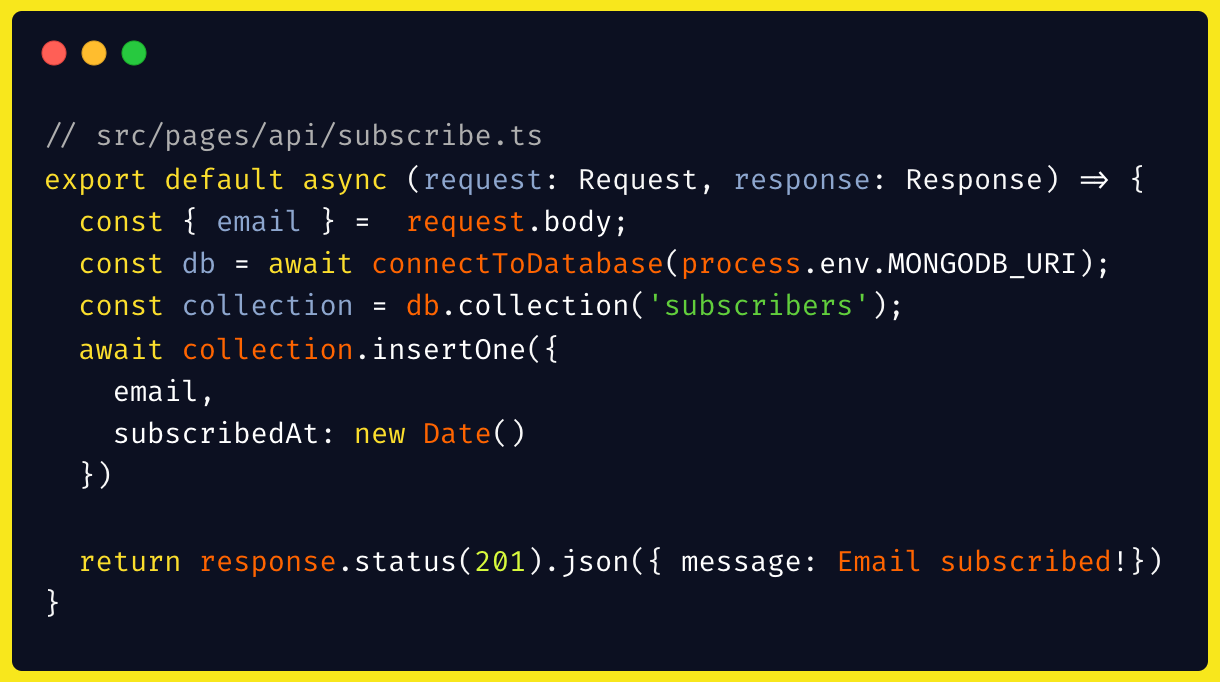
Thanks to this kind of approach, we can develop a front end application that navigates through different architectures. Some pages are SPA and will request resources at runtime, others are SSR and will process all server side resources, and others are SSG and process best side at build time. The modern backend is a Javascript function.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of serverless computing?
PROS:
-
Simpler resource allocation: tasks associated with servers, such as provisioning, scaling, and managing the infrastructure needed to run the application, are no longer a concern and occur automatically in the background. Thus, the simplicity of resource allocation is one of the great advantages of a serverless architecture.
-
Development efficiency: in the initial example, you will have more time to think about the core of the application and deliver more value to the users. This also means developers can build applications faster than in traditional environments.
-
Dynamic scaling: for me, one of the best advantages of these services. The entire structure of servers, networks, containers, databases, etc, etc, etc, can be quickly expanded (or reduced) according to current demand. Thinking about Amazon, practically everything is already pre-configured for use.
-
Faster deployment: ease of deployment factors in as a major benefit. Traditional data center-based operations consume months in selecting, procuring, and deploying physical equipment. Serverless computing, on the other hand, can deploy in a few hours.
CONS:
-
Less control: not running your own server or controlling your own server-side logic can have drawbacks.
-
Restrictions of each service: cloud providers may have strict constraints on how their components can be interacted with, in turn affecting how flexible and customized your own systems can be. In the case of BaaS environments, developers may be beholden to services whose code is outside their control.
-
Dependency: ceding control of these aspects of your IT stack also opens you up to vendor lock-in. Deciding to change providers will also likely come with the cost of upgrading your systems to adhere to the new vendor’s specifications.
Depending on the size and on the timing of your application, cost can be an advantage or a disadvantage. The services work on demand and TO GET YOUR MONEY on demand.
Quick idea validation! Most BaaS and FaaS services are free initially. It is possible to build great ideas, abstracting the complexity of the infrastructure and focusing more on the product that will be built. A great environment to test, study and validate projects, for sure. Every time you spend time with infrastructure, you have less time to generate value for the end users.
Conclusion
Fortunately, following trends topics, we will talk more about serverless in the future and learn about concrete cases. So I'm open to talking about it and going deeper and deeper into this article. See you and take care!